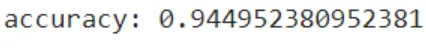In supervised machine learning, there is a plethora of machine learning models like linear regression, logistic regression, decision tree and others. we use these models to resolve classification or regression problems, and ensemble learning is a part of supervised learning that gives us models that are built using several base models. Random forest is one of those ensemble learning models that are popular in the data science field for its high performance.
Technically, random forest models are built on top of decision trees and we have already covered the basics of a decision tree in one of our articles, so we recommend reading the article once to understand this article’s topic clearly. In this article, we will talk about random forests using the following points.
Table of content
- What is Random Forest?
- How Does a Random Forest Work?
- Important Features
- Important Hyperparameters
- Code Example
- Pros and Cons of Random Forest
What is Random Forest?
Random forest is a supervised machine-learning algorithm that comes under the ensemble learning technique. In supervised machine learning, a random forest can be used to resolve both classification and regression problems.
As discussed above that, it comes under the ensemble learning technique, so it works on top of many decision trees. We can say that decision trees are the base model of a random forest. The algorithm simply builds many decision trees on different data samples, and using the majority vote system solves the classification problem. In the case of regression, it uses the average of the decision trees.
How does a Random Forest Work?
When we talk about the working of the random forest, we can say that it gives outcomes by ensembling the results of many decision trees. Here if we talk about a classification problem, each decision tree predicts an outcome and whatever the class gets majority votes comes out as the final result of a random forest. Let’s take a look at the below image.

When we talk about the working of the random forest, we can say that it gives outcomes by ensembling the results of many decision trees. Here if we talk about a classification problem, each decision tree predicts an outcome and whatever the class gets majority votes comes out as the final result of a random forest. Let’s take a look at the below image.
The above image also gives the intuition behind the ensemble learning technique, where the final prediction is made by combining the results of several other models. The ensemble learning technique can be followed using two ways:
- Bagging: this way, we divide data into various subsets and train the base models like decision trees in a random forest, and the majority vote for any class comes out as the final result.
- Boosting: this way, we combine weak learners with strong learners and make a sequence of the model so that the final model is most accurate amongst every learner. For example, XG boost and ADA Boost models.

Random forest in ensemble learning uses the bagging method. We can say that every decision tree under the random forest uses a few samples from the whole training data to get trained and give predictions. Let’s talk about the steps involved in training the random forest algorithm.
Steps involved
- First, it extracts n number of subsets from the dataset with k number of data points that we call n subsets.
- n number of decision trees are constructed to get trained using n subsets.
- Each decision tree gives predictions.
- Final predictions are generated using the majority voting system for the classification problem and an averaging system for the regression problem.
Using the above four steps working of a random forest gets completed. Next, let’s discuss the important features of a random forest.
Important features
- Highly immune to dimensionality: Since all data features are not considered in the making of decision trees, the whole random forest gives high performance even in a situation where data is high-dimensional.
- Diversity: every decision tree uses some of the features from the data. That’s why the training procedure becomes different for the different decision trees. At final, we get more optimum results.
- Data split: while making a random forest, we don’t really need to spit data in train and test because there will always be some percentage of data unknown for a decision tree.
- Stable: random forests are stable algorithms when modelled because the majority voting or averaging system is used to make the final prediction.
- Parallelization: as we know, every individual decision tree uses a part of the main data. It makes full use of the CPU to train random forests.
- No overfitting: as the final results from the random forest come from the majority voting or averaging system and the decision tree uses subsets to get trained, there are fewer chances of overfitting.
Important Hyperparameters
In the above we have discussed the working and features of random forests, here we will discuss the important hyperparameters of any random forest using which we can control the random forest while increasing its performance and making it’s working or calculation faster.
- n_estimators- The number of decision trees required to build the random forest.
- max_features- Maximum number of features that random forest will use from data to split the data.
- mini_sample_leaf — minimum number of leaves is required to split the decision tree node.
- n_jobs — we use it to speed up the calculation of random forest because it tells the number of processors a system needs to train the model.
- random_state- just like for other models, it controls the randomness of the sample.
Code Example
In the above discussion, we have seen how random forest work and their important hyperparameters. Now after knowing this, we need to know how it works using any tool. So here we will look at the simple implementation of the random forest using the python programming language.
We will use randomly generated data and the sklearn library in this implementation. So let’s start with generating data.
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X,y = make_classification(n_samples = 2000, n_features = 6, n_informative = 3)
print(‘data features n’,X)
print(‘data_classes n’, y)
Output:

Here we can see features and classes of randomly generated data. In the making of data, we have generated 2000 samples that have 6 features and one target variable.
Let’s build a model
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
clf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth = 4, random_state = 42)
Here we have created an object named clf that consists of a random forest classifier. Let’s train the model.
clf.fit(X,y)
print(‘count of the decision trees :’,len(clf.estimators_
Output:

Here we can see that 100 decision trees are under the random forest. Now we can draw a decision tree from our random forest using the following lines of code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10
tree.plot_tree(clf.estimators_[0],max_depth = 2)
plt.show()
Output:

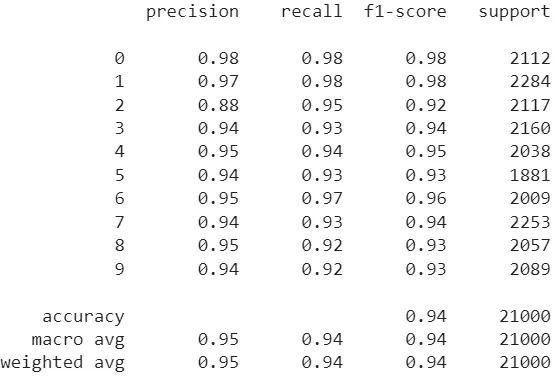
Here we have implemented a random forest, and to increase the explainability, Now we can draw a decision tree from a random forest using the following lines of code:
print(clf.predict([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
print(clf.predict([[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]]
Output:

Now results from the model are in front of us and this is how we can implement a basic random forest. Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of the random forest algorithm.
Pros and Cons of Random Forest
Pros
- We can use it for both classification and regression problems.
- It does not overfit.
- It can also work with data that contains null values.
- High-performing with high dimensional data.
- It maintains diversity in the results.
- Highly stable.
Cons
- Random forest is a highly complex algorithm.
- Training time is more because it takes more time to calculate, develop and train decision trees.
Final words
Under the series of articles, this article consisted the information about the random forest, which is a machine learning algorithm used to resolve problems that come under supervised learning. In the article, we have discussed the what, why and how of random forests. Using an example we looked at its implementation. Looking at the pros and cons of this model, we can say that it has such features and functionality that gives us higher accuracy. Still, before using this model we should understand the basic concept behind the model so that we can tune it appropriately.
About DSW
Data Science Wizards (DSW) is an Artificial Intelligence and Data Science start-up that primarily offers platforms, solutions, and services for making use of data as a strategy through AI and data analytics solutions and consulting services to help enterprises in data-driven decisions.
DSW’s flagship platform UnifyAI is an end-to-end AI-enabled platform for enterprise customers to build, deploy, manage, and publish their AI models. UnifyAI helps you to build your business use case by leveraging AI capabilities and improving analytics outcomes.
Connect us at contact@datasciencewizards.ai and visit us at www.datasciencewizards.ai